Introduction
Do you know, “What is serial interface?” It is a data transmission method where data is sent sequentially, one bit at a time, over a communication channel. It has applications from personal computers to industrial automation.
A data transmission interface is the communication pathway between two devices. It maintains a physical and logical connection between the devices which enables digital information interchange.
In this article, you will learn the fundamentals of serial interfaces, including their types, advantages, and disadvantages. Let’s begin.
Article Directory:
- Introduction
- What is Data and Data Transfer technology
- What is Serial Interface?
- Types of Serial Interface
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Serial Interface
- FAQs
- Conclusion
What is Data and Data Transfer technology?
Before discussing the serial interface, let’s learn the basics of data and data transfer technology.
Data is any information that can be stored or communicated. It includes text, numbers, images, audio, and video. All data is stored in binary form as 1s and 0s. Computers process data using these binary bits. Each bit represents a single piece of information. Eight bits together form a byte, which can store one character of text.
Electronic devices use transistors to convert data into binary. These transistors are like switches, and they can be either “on” (1) or “off” (0). The binary bits (1 and 0)are the basis of data transfer technology.
Data transfer is the movement of data between devices or systems. It happens over cables, wires, or wireless signals. The speed of data transfer depends on the technology used. Common data transfer methods include USB, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and Ethernet. USB is great for short distances, while Wi-Fi works well for wireless connections.
Data transfer rates are measured in bits per second (bps). Faster speeds mean quicker file sharing and downloads. Modern technology supports gigabit-speed transfers. Advances in technology keep improving data transfer speeds. Fiber optics and 5G are examples of fast and modern data transfer solutions. They make communication between the devices faster and more reliable.
Wireless data transfers have some safety features. Protocols like TCP/IP manage how data moves across networks. These rules ensure data reaches the right destination safely. Data could get lost or mixed up without protocols.
Another data important data safety feature is encryption. Encryption protects data during transfer. It scrambles information to prevent unauthorized access. Securing data transfer is vital for privacy and online safety.
Understanding data and its transfer technology helps us use modern technology better. It’s the foundation of everything we do online, from emails to streaming videos.
What is Serial Interface?
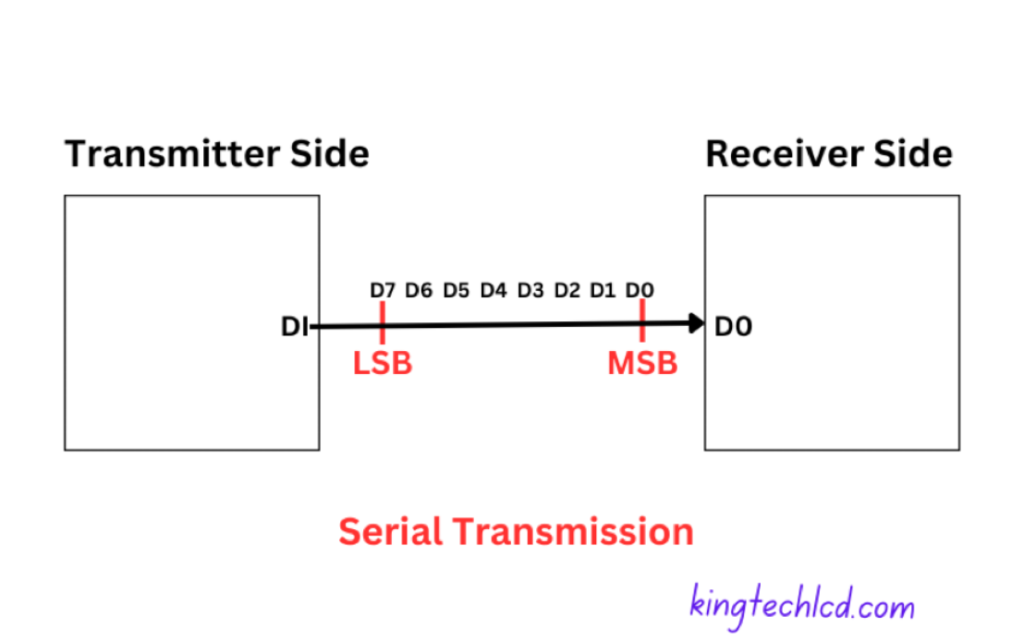
The serial interface is a data transfer technique to send data one bit at a time between two digital devices. It sends data as the pulse of voltage. The high voltage is considered the logical 1 and the low voltage is the logical 0.
Serial data transfer requires fewer wires than parallel interfaces. This makes it simpler and cheaper to build. It’s commonly used in USB, HDMI, and RS-232 connections.
Data bits are sent in a sequence, like cars on a single-lane road in a serial interface. The receiver reads the bits in the same order they were sent.
Types of Serial Interface
There are two main types of serial interfaces: synchronous and asynchronous. Synchronous uses a clock signal to sync data. Asynchronous adds start and stop bits to each byte. Both types are widely used in modern times.
Asynchronous Serial Interface (SCI)
Data is transmitted in a frame in an asynchronous serial interface. The frame has a defined start and stop bit to mark the beginning and end. This helps the receiver know when to read the data. A typical frame includes a start bit, 7 or 8 data bits, a parity bit for error checking, and a stop bit. This structure ensures reliable data transfer.
The SCI sends data one bit at a time without a shared clock signal. When the data is sent in this interface, the start bit sends signals for the receiver to start reading. The receiver then reads each bit at regular intervals based on the baud rate. The parity bit checks for errors by confirming if the number of 1s in the data is even or odd. If there’s a mismatch, an error is detected.
After sending the last data bits, the stop bit signals the end of the frame. This prepares the receiver for the next set of data.
SCI data transfer technique is easy, reliable, and cost-effective. It works well in short-distance communication like a computer to a printer or keyboard. It reduces the complexity of wiring and setup. SCI can communicate independently without strict synchronization.

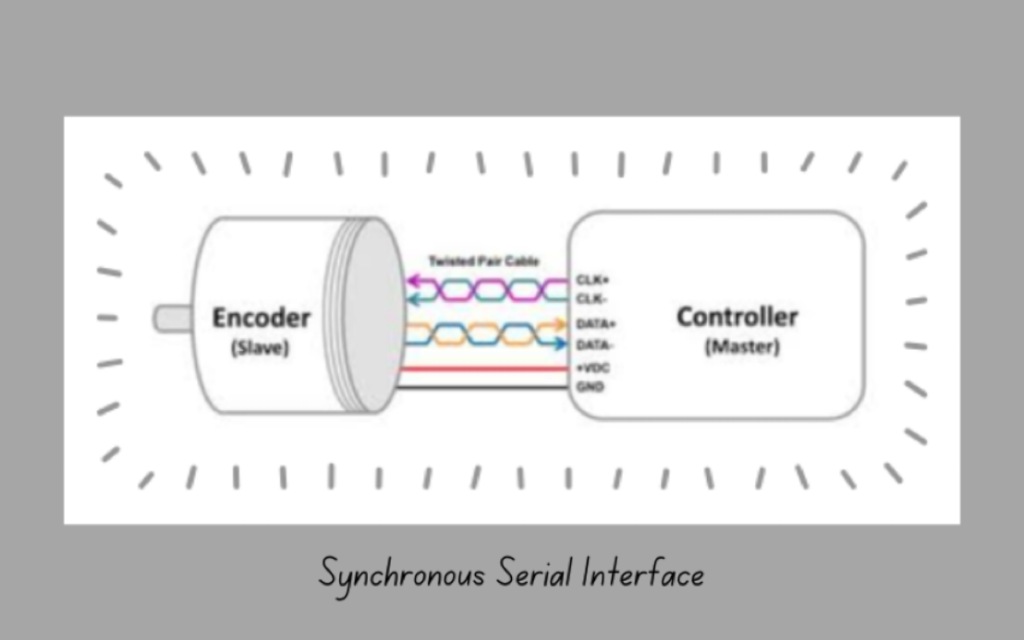
Synchronous Serial Interface (SSI)
The synchronous serial interface has a shared clock system in their data sender and receiver. Here the data is transferred as a continuous stream using the common clock signal. The SSI data transfer method ensures that the transmitter and receiver are synchronized. This synchronization ensures efficient and reliable data transfer.
The clock signal of the SSI system can be generated by either the transmitter or an external source depending on its configuration. The data in the system is organized into many frames. The frames contain start bits, data bits, and sometimes stop or error-checking bits. The frame structure describes the starting and ending of the data packets in SSI.
The SSI interface can run in full duplex and half duplex mode. The full duplex mode is for transmitting and receiving data simultaneously and the half duplex mode is for transmitting or receiving data at one time.
Some SSI interfaces have error detection mechanisms like parity bits or cyclic redundancy checks(CRC) to ensure data integrity. The SSI is usually used in high-speed and reliable data transfers in telecommunications, networking, and industrial automation. It has limitations in multi-device systems and clock skew issues in long-distance transmission.
The Serial Peripheral Interface(SPI) protocol is an example of an SSI system. This embedded SPI protocol is widely used in communication between microcontrollers and peripheral devices like sensors, SD cards, and displays.
We hope you are now clear about what is serial interface.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Serial Interface
The serial communication interface has several advantages and some disadvantages. In this section of the article let’s look over the facilities and limitations of this interface.
Advantages:
- Lower Cost:The serial interface is less costly than the other communication interfaces because of less wire requirement, lower implementation costs, and simple hardware.
- Long Distance Communication:Serial communication is suitable for long-distance data transmission with minimum signal degradation.
- Reduced Interference:The single-channel transmission makes the data transmission less prone to electrical interference.
- Scalability:The serial interface is easily scalable with different devices of a serial network.
- Simplicity:Serial communication protocol is easier to implement than other communication interfaces.
Disadvantages:
- Slow Data Transfer Rate:The serial interface sends one bit of data at a time resulting in slower transmission speeds compared to parallel interfaces.
- Protocol Complexity:It requires additional protocol overhead for synchronization and error detection.
FAQs
The following frequently asked questions will help you understand the context of what is a serial interface.
Q. What are the examples of serial interfaces?
The following are the most used serial communication interfaces:
<p The text states that the most used serial communication interfaces are:
- I²C
- SPI
- UART
- RS232 Labview
- Rs-422 pinout
- USB to RS 485
- EIA 485
- 3-wire serial interfaces
- ADC serial interfaces
- RS485 Cable
- USB
- CAN
- Ethernet
Q. What is serial interface?
The serial interface is a communication interface or channel in the electronic industry where data is transmitted over a single wire one bit at a time. It is a different technique from parallel communication where multiple channels are used to transfer the data.
Q. Are serial interfaces still used?
Yes, serial communication technology is still used in low-speed and simple data transfers. It is popular for its simplicity and cost-effectiveness. It is mostly used in long-distance communication, embedded systems, and traditional devices such as scientific equipment, automation, point-of-sale systems, and consumer products.
Conclusion:
So, friends, it’s time to sum up! We have covered a detailed explanation to clarify the topic “What is serial interface”. Serial communication is a traditional communication interface with applications in many modern devices and systems. It has made data transmission simple and easy.
We hope you enjoyed learning about the serial communication interface. Thank you!
