Introduction
This article will explain how LCD display works, their working principles, and their types. Let’s dive in.
In This Article:
- Introduction
- How LCD Display Works? Detail Explanation!
- Basic of Liquid Crystals
- What is Backlight and How Does it Work?
- What is a Liquid Crystal Layer, and What is its Role in LCD Display Technology?
- What are Color Filters and Their Function in LCD Technology?
- Different Types of LCDs
- FAQs
- Conclusion
How LCD Display Works? Detail Explanation!
We first learn the basics of LCDs which are liquid crystals. If you want to understand how LCD display works, you should have the proper knowledge of liquids and crystals.
Basic of Liquid Crystals
The name liquid crystals may seem contradictory. Crystal is a solid, hard material like stone, and liquid is like water. Understanding how these two different materials are attached is essential to understanding how LCDs function.
We know matter has three states: solid, liquid, and gaseous. The molecules of the solid material maintain a stable orientation and position which means solid molecules are fixed in their position inside the matter.
On the other hand, molecules of liquids can change their orientation anywhere in the liquid.
You will be perplexed to know that some substances act like solids and liquids together in a chemically odd state. In these states, their molecules try to stay in a fixed orientation like the solid and shift to other positions like liquid. Here is the twist of liquid crystals. It is not like a solid or liquid directly but possesses the characteristics of both.
Liquid crystals are more like liquids than solids. They need much less heat to change their state to liquid, so they are temperature-sensitive. For this reason, your laptop display may show some weird characteristics on hot summer days and too-cold winter days.
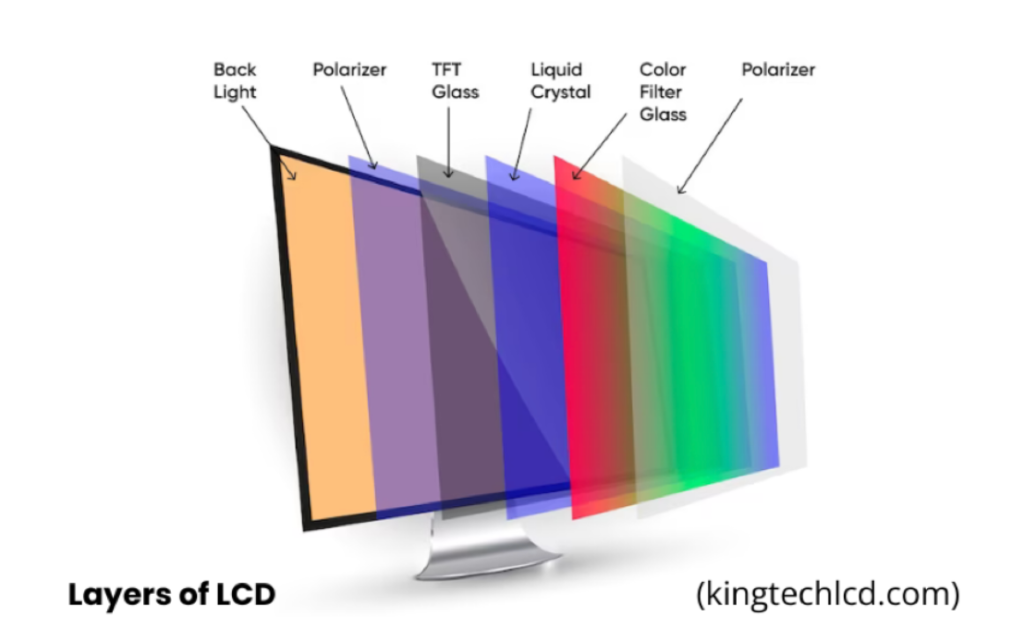
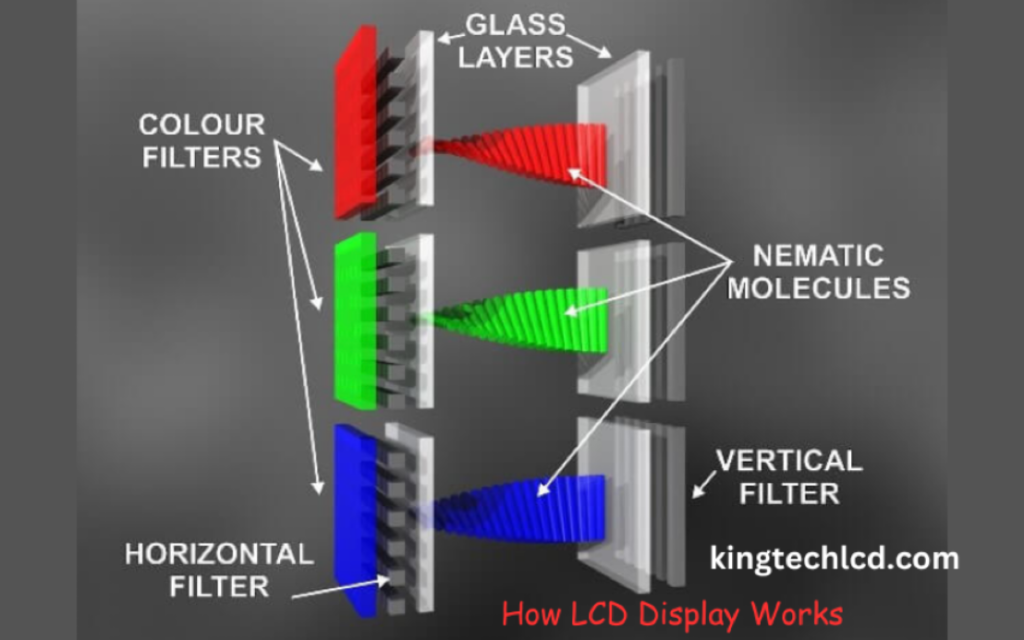
So, How LCD Display Works?
LCDs work based on three basic components such as:
- The backlight
- The liquid crystal layer
- And the color filters
What is Backlight and How Does it Work?
The backlight is the source of light that provides the necessary light supply to the LCD display. Liquid crystal cannot manipulate light accurately to generate images without the backlight technology.
The backlighting technology enlightens the pixels of the display and makes the photo visible to spectators. The light source of the backlight technology is some LED lamps enclosed on a panel across the display called the diffuser. This diffuser diffuses light to pass through the polarized filters and a liquid crystal layer which uses light to generate the pictures.
Backlighting techniques depend on four major steps: light generation, diffusion, manipulation, and polarization. Each step is crucial for producing clear, vibrant, and perfectly colored images on the display.
What Is a Liquid Crystal Layer, And What Is Its Role in LCD Display Technology?
Liquid crystals are the major elements of LCDs. The liquid crystal layer consists of many tiny cells filled with liquid crystals. These liquid crystals exchange their orientation when electricity is applied. Light is emitted by the backlight technology and passes through the liquid crystals.
By controlling the amount of light that passes through these crystals, we can create different shades of color. The combination of these color shades and the backlighting is used to generate images on the LCD.
What are Color Filters and Their Function in LCD Technology?
The LCD can represent vibrant colors for the color filters. Color filters assemble the color of the images generated by the liquid crystal layer. Every pixel of the LCD contains three sub-pixels with red, green, and blue filters. These sub-pixels generate a huge color spectrum together.
The liquid crystals monitor and fix the amount of light that can go through the color filters and designate the display color. Here is the breakdown of the color filter working process:
- Step 1: The backlight of the LCD panel transmits white light.
- Step 2: The color filter layer placed in front of the backlight allows specific colors of light to pass through it. This filter contains numerous tiny filters arranged in a pattern or stripes known as pixels.
- Step 3: The liquid crystal layer behind the color filters regulates light passage through the filters. It allows or blocks the light. These crystals perform color filtering using an electric field.
- Step 4: Different color formation occurs in this stage. The white color emitted from the backlight is filtered into red, green, and blue components. The liquid crystal layer controls the color intensity and displays different colors on the screen.
- Step 5: A wide range of colors is created in this step by changing the intensity of subpixels(red, green, blue). This color combination makes it possible to generate vivid color images in the LCDs.
I hope you are now clear about how LCD display works to produce colorful images with LCD screens.

Different Types of LCDs
Different types of LCDs are available for various needs. The Twisted Nematic (TN), In-Plane Switching (IPS), and Vertical Alignment (VA) are the commonly used LCDs.
1. Twisted Nematic (TN) LCDs:
TN LCDs are the earliest and most common. They work on twisting liquid crystals by 90 degrees between the glass substrates. TN displays have fast response times, limited viewing angles, and color reproduction. They are ideal for gaming devices.
2. In-Plane Switching (IPS) LCDs:
IPS displays have wider viewing angles and excellent color accuracy compared to TN panels. They are popular for high-resolution works like photo and video editing, and graphic design. When voltage is applied on the IPS technology, the liquid crystals allow them to rotate horizontally and arrange the liquid crystals parallel to the glass substrates.
3. Vertical Alignment (VA) LCDs:
In VA panels, the liquid crystals are perpendicular to the substrates. When voltage is applied to it, the crystals reverse their position to allow light to pass through them. VA technology offers better contrast ratios and color accuracy than TN and IPS panels but has lower response times.
FAQs
Is LCD better than LED?
Both LCD and LED technologies have their advantages and disadvantages. The choice between them depends on your specific needs.
If you prioritize excellent picture quality, along with higher contrast ratios, color accuracy, and brightness, then LED is the better option.
On the other hand, if you’re on a budget but still want good image quality, LCDs are more suitable. However, never forget their color accuracy and contrast ratios may not match those of LED displays.
Is LED or OLED better?
OLED is an updated version of LED. It has a faster response time, a high refresh rate, and better color accuracy than the LED.
Is LED or QLED better?
QLED is superior to LED technology. The picture quality of QLED(Quantum LED) is better than that of standard LEDs. The quantum dot technology in QLED provides more vivid colors than typical LEDs.
Which lasts longer, LCD or LED?
LED displays last longer than the LCD displays. The average expected life span of an LED display is around 100,000 hours while the life of an LCD display is 50,000 hours.
The reason behind this long-lasting LED technology is the durability of the light-emitting diode. The diodes of LED displays have a longer lifespan than the traditional fluorescent light of LCDs. LED generates less heat than LCD, which also extends their lifetime.
Hence the LEDs last longer than the LCD.
Conclusion
LCD screen technology has made the viewing experience enjoyable. LCDs have wide applications in aircraft cockpit displays, calculators, digital cameras, computer monitors, wristwatches, mobile phones, etc. Understanding how LCD display works will help you make an informed decision to purchase.
The primary use of LCDs in televisions is to provide an immersive and realistic viewing experience. LCDs are affordable, energy-efficient, have a long lifespan, are less prone to burn-in compared to OLEDs, and can achieve high refresh rates.
We hope this article has clarified the principles of LCDs. If you have any questions or doubts about LCDs, please write to us in the comments section.

