Introduction
Display technology is an essential element of electronic devices and gadgets. From its inception to the present, displays have significantly evolved into more efficient models. IPS is one of the popular display technologies for many reasons. It was invented in the ’90s to solve color and viewing angle issues.
The present IPS display offers amazing colors, wide viewing angles, and higher brightness, at a reasonable cost. The IPS LCDs are used widely in computer monitors (laptops and desktops), smartphones, tablets, televisions, medical imaging, gaming monitors, digital signage, etc.
However, this article will explain what does IPS stands for and how it operates. Let’s start.

Article Directory:
- Introduction
- What Does IPS Stand For?
- How Do IPS Displays Work?
- How Does the IPS Display Create Image?
- Advantages of IPS Displays
- Disadvantages of IPS Displays
- FAQs
- Conclusion
What Does IPS Stand For?
The IPS monitor is a customized LCD monitor. IPS stands for In-Plane Switching. It is a display technology used with Liquid Crystal Displays (LCDs) to change the usual characteristics of the liquid crystals to generate sharp, vivid, and accurate pictures.
IPS displays can deliver better pictures than TN LCD (twisted nematic) and VN LCD (vertical alignment) displays. It has wide applications from personal computer monitors to wearable devices like smart watches.
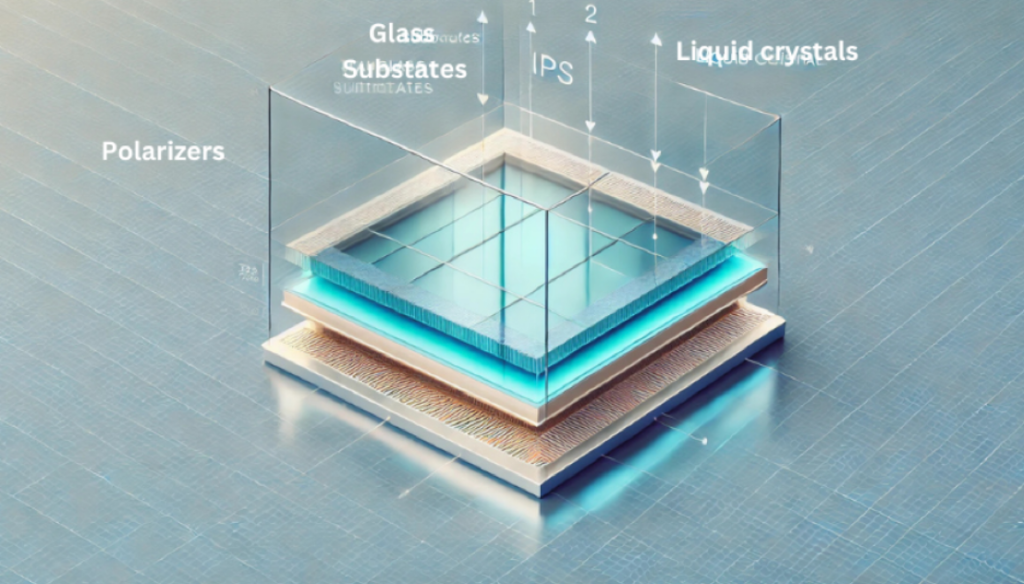
How Do IPS Displays Work?
We learned what does IPS stand for and now let’s see how it works.
The basic element of IPS panels is the liquid crystals of the LCD technology. Liquid crystals are organic compounds that act like liquids but have the same molecular orientation as crystals. The liquid crystals of the IPS panel are controlled to manage light passage with the application of electricity.
In an IPS display, the liquid crystals are oriented parallel to the glass surfaces. When electricity is applied, the liquid crystals twist and rotate within the same plane instead of aligning perpendicularly. This in-plane rotation is the fundamental principle behind IPS technology.
How Does the IPS Display Create Image?
The IPS display creates images through a precise combination of backlighting, liquid crystal manipulation, and color generation.
There is a backlight(usually LEDs) or mirror behind the polarizer of the IPS display. The image generation starts with this uniform light source(backlighting). This backlighting technology emits light to illuminate the display.
The light then passes through the liquid crystal layer sandwiched between two glass substrates. The glass substrates are transparent layers to house and support the liquid crystals. They also hold the thin film transistors(TFTs) and electrodes.
There are polarizers on either side of the liquid crystal layer attached to the outer surface of the glass substrates. These polarizers control the orientation of the light waves.
The first polarizer ensures that only light waves with a specific alignment enter the liquid crystal layer. The second polarizer collaborates with the liquid crystals to control how much light exits each pixel, depending on the alignment of the crystals.
The liquid crystals remain parallel and aligned with the screen surface. The alignment is controlled by precise electrical charges supplied from the TFT layer. These charges adjust the orientation of the crystal to regulate the angle and amount of light passing through the crystals.
Polarizing filters on either side of the liquid crystals allow the properly aligned light waves only to pass through them and control the darkness and brightness.
The TFT layer and the electrical signals in the display determine the intensity of the RGB(red, green, and blue) subpixels. The TFT layer applies precise voltages to each subpixel in a pixel.
These applied voltages control the alignment of the liquid crystals corresponding to each subpixel. It also determines how much light can pass through the red, green, and blue parts of the pixel.
This whole process happens quickly and allows the screen to update new images many times per second.
Finally, the IPS display mixes red, green, and blue light in different proportions to create the desired color by varying the light intensity for each subpixel. The combination of light, liquid crystals, and RGB subpixels creates the image on the screen together.
For example, if the screen needs to show yellow, it increases the brightness of the red and green subpixels and dims the blue subpixel in that area. This same process happens for every pixel across the screen, creating the full picture you see.
I think you are now clear about “what does IPS stand for” and how IPS works. If you face any difficulties while learning, please don’t hesitate to reach us.

Advantages of IPS Displays
IPS displays offer several key advantages over traditional LCD technologies.
- Superior Color Accuracy: IPS panels are renowned for accurate and consistent color creation. They are popular among professionals such as graphic designers, photographers, and video editors.
- Wide Viewing Angles: IPS displays have wide viewing angles compared to the other LCD types. The display can maintain consistent image quality regardless of the viewer’s position or angle.
- Enhanced Visual Experience: The IPS display provides accurate color reproduction and wide viewing angles for an enhanced visual experience.
- Visibility in Direct Sunlight: The IPS LCDs provide the best visible images in direct sunlight. The high-power LED backlights and unparalleled viewing angles made them perfect for daylight use.
Disadvantages of IPS Displays
The IPS displays have some disadvantages. The referable drawbacks of an IPS display are:
- Higher Cost: IPS displays are more expensive than other display types such as TN (Twisted Nematic) or VA (Vertical Alignment) displays. The complexity of the manufacturing technology has made them costly.
- Slower Response Times: IPS panels generally have slower response times than TN panels. This can lead to slight motion blur in fast-paced games or videos. Hence, they are not ideal for different high-responsive tasks.
- Higher Power Consumption: IPS displays consume more power, especially when displaying bright or vivid-colored content. This in turn reduces the battery life of the portable IPS LCD devices.
- Lower Contrast Ratio: The contrast ratio of IPS panels is lower than that of VA panels. This means blacks may appear more like dark gray. It reduces the depth of dark scenes in movies or games.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The following FAQs will help you learn more about what does IPS stand for and its applications.
What is better, IPS or LED?
Both IPS and LED displays have their advantages and disadvantages.
IPS monitors have better color accuracy, wider viewing angles, and consistency. They are ideal for tasks that require precise color representation, such as graphic design and video editing. IPS displays allow viewing content from different angles.
In terms of brightness, LED monitors outperform IPS monitors. LED monitors are brighter and more energy-efficient than IPS monitors. Additionally, LED monitors offer better durability and affordability compared to IPS monitors.
However, IPS monitors are also not good at handling fast motion like other display technologies. They are good for office work, movie watching, and games.
Which is better IPS or AMOLED?
IPS displays are more affordable and easier to manufacture than AMOLED displays. Additionally, IPS LCDs tend to be brighter and offer better visibility compared to AMOLED displays.
The IPS LCD also has better off-axis viewing angles than AMOLED.
Nevertheless, the IPS display requires more backlight to operate, resulting in higher power consumption. The AMOLED displays on the other hand have longer battery life.
What does IPS stand for?
The acronym IPS stands for In-plane Switching. It is a special type of LCD panel renowned for high resolution and bright color production.
Which is the best display type?
OLED(Organic light-emitting) displays are considered the best for picture quality and design flexibility. The OLEDs offer true blacks, excellent color, infinite contrast ratios, and wide viewing angles.
Which type of display is best for eyes?
OLED displays are considered the best for the eyes due to their lower blue light emission, higher contrast ratios, and minimal PWM flicker. These characteristics of the OLED displays significantly reduce eye strain compared to traditional LCD screens.
Should I buy an OLED or IPS laptop?
Both the OLED and IPS monitor laptops have some advantages and disadvantages. The following are the key considerations to select OLED and IPS displays:
Pros of OLED: OLED displays have excellent contrast ratio due to true blacks, Vibrant colors, thinner and lighter design, and the potential for better HDR quality pictures.
Cons of OLED: OLED has some drawbacks such as higher price, prone to burn-in, and high power consumption.
Pros of IPS: IPS monitors offer good color accuracy, and wide viewing angles, and are more affordable than OLED.
Cons of IPS: It has less deep blacks and slower response times compared to OLED.
When to choose an OLED: If you are a content creator, gamer, or movie lover who needs precise color reproduction, and a satisfactory visual experience, you can buy an OLED laptop.
When to choose IPS: If you have a budget constraint and use a laptop for office work that requires high peak brightness, consider purchasing an IPS monitor.
Conclusion on “What does IPS stand for”
IPS displays have revolutionized the visual experience on our electronic devices. They have become popular display types for their color accuracy and wide viewing angles. We expect IPS displays will become more efficient soon.
However, understanding what does IPS stand for and the working procedure of the IPS display will keep you ahead as a modern technology user. We hope you enjoyed reading the whole article and stay connected with us.

